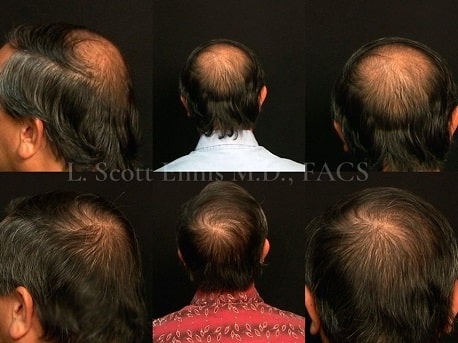
Male pattern hair loss, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is a common condition that affects men. It is characterized by a receding hairline and thinning of the hair on the crown and temples. Male pattern hair loss is caused by a combination of genetics and hormones, and it is typically progressive, meaning that it gets worse over time.
There are several medical treatment options available for male pattern hair loss, and the most appropriate option will depend on the severity of the hair loss and the individual's goals.
Medication
One common treatment option is medication. There are several medications available that are specifically designed to treat male pattern hair loss, and they work by inhibiting the production of a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is believed to play a role in hair loss.
- Finasteride (Propecia) is a prescription medication that is taken orally and is specifically designed to treat male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the production of DHT, which can help to slow or stop hair loss.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine) is a topical medication that is applied directly to the scalp. It is available in both a foam and a liquid form and is specifically designed to treat male pattern baldness. It works by increasing blood flow to the hair follicles, which can help to stimulate hair growth.
It's important to note that both finasteride and minoxidil are prescription medications and should only be used under the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider. They are generally considered safe and effective when used as directed, but like any medication, they can have potential side effects and may not be suitable for everyone. It's important to discuss the potential risks and benefits of these medications with a qualified healthcare provider before starting treatment.
Hair Transplant
Another treatment option for male pattern hair loss is hair transplantation. During a hair transplantation procedure, the surgeon will remove individual hair follicles from a donor area of the scalp (such as the back or sides of the head) and transplant them to the recipient area (the area of the scalp that is thinning or balding).
The surgeon will carefully select the follicles to ensure that they are healthy and will thrive in the recipient area. Hair transplantation can be an effective treatment option for male pattern hair loss, but it is a surgical procedure and does carry some potential risks and complications, such as infection, scarring, and the possibility of the transplanted hair falling out although these risks are very rare.
Summary
In summary, male pattern hair loss is a common condition that can be treated with medication or hair transplantation. Finasteride (Propecia) and minoxidil (Rogaine) are two common medications that are used to treat male pattern hair loss, and they work by inhibiting the production of DHT or increasing blood flow to the hair follicles.
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure that involves the removal and transplantation of individual hair follicles to the recipient area. Both treatment options are generally considered safe and effective, but like any medical treatment, they can have potential risks and complications.
It's important to discuss the potential risks and benefits with Dr. L. Scott Ennis, a qualified and experienced hair restoration healthcare provider before starting treatment.